DDR5 I3C
What is the role of the I3C Protocol in DDR5?
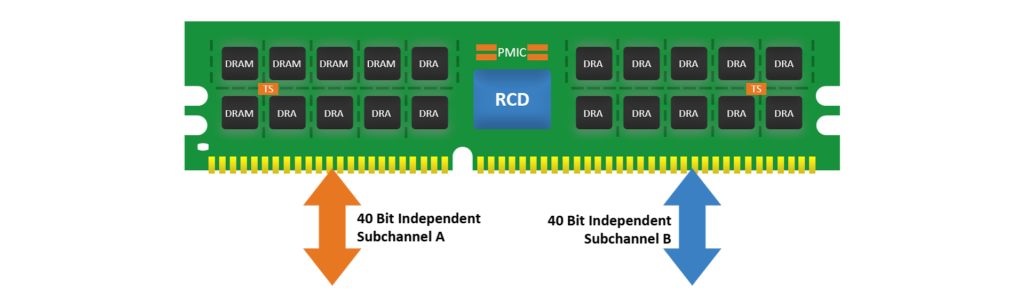
DDR5 has significant improvement over DDR4. DDR5 offers higher bandwidth with a data rate of up to 6.4 Gbps and operates at 1.1V consuming lower power compared to DDR4. The channel architecture is also significantly different compared to DDR4. DDR5 has two independent channels, unlike DDR4. To support additional performance and monitoring there are some interesting features as well.
Temperature Sensor IC on DIMM
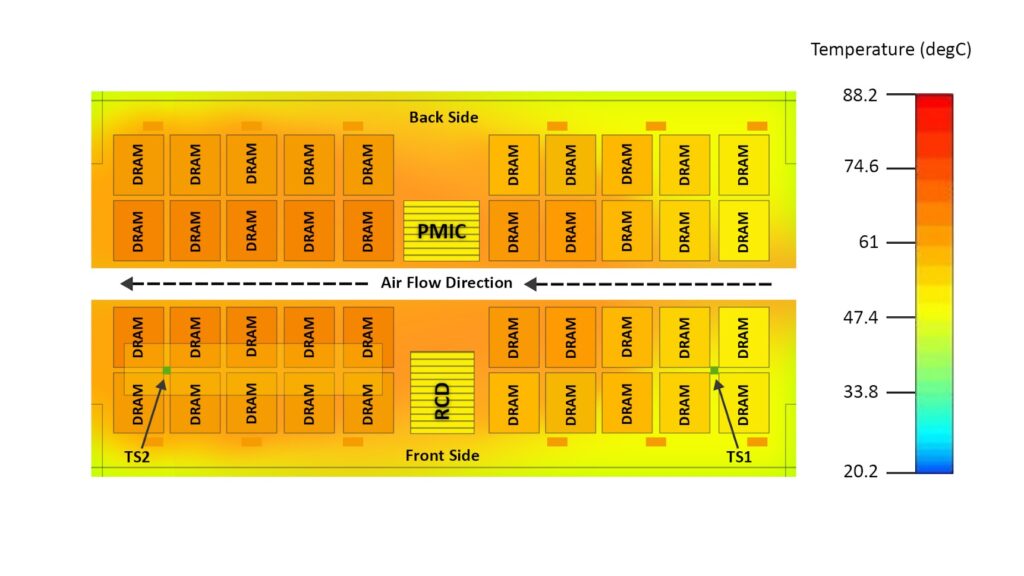
DDR5 has two IC for temperature sensors TS1 and TS2. The purpose of these sensors is to monitor thermal changes in DIMM. Each of these DIMMs is strategically placed at the end of the DIMM to get the complete thermal profile of the DIMM. These temperature sensors use I3C interface Temperature sensors TS1 and TS2 can be controlled for fan speed changes and ensure the temperature profile is correctly maintained in the DIMM.
Image of DIMM with Temperature sensor.
Side Band Access:
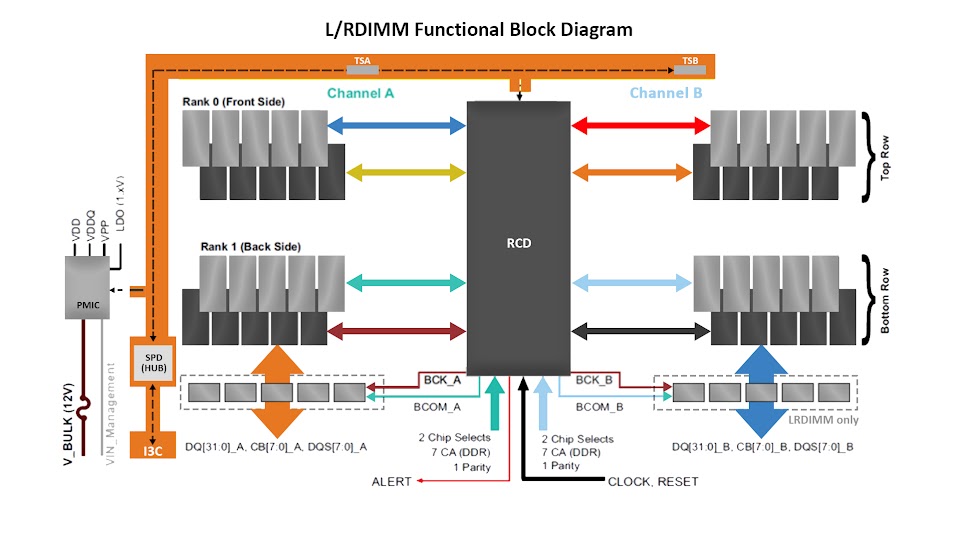
DDR5 introduced a sideband bus to access non-DRAM modules. The Sideband bus is based on MIPI I3C or I3C Protocol. Apart from the sideband bus, there is also an SPD ie Serial Presence Detect Hub as the number of components has grown on DDR5. The SPD Hub interfaces the internal components of DIMM like RCD ie Register Clock Driver and PMIC and another temperature sensor IC.
Image of the Sideband bus
Debugging I3C Interface:
Prodigy has developed state of the art I3C Protocol analyzer. The I3C Protocol analyzer can be used to Debug the I3C Sideband bus in the DDR5 as well it can be used to check the protocol compliance of temperature sensors.