ARE PCIE AND NVME THE SAME?
PCIe and NVMe are two terms that are often heard together. Almost all the latest motherboards support the PCI Express x4 NVMe M.2 drives but may vary from board to board. NVMe is specifically designed to work with the latest solid-state drivers to utilize its full potential. It replaced the AHCI control scheme which also works with SSD but was originally designed to work with old hard drives.
What is PCIe?
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) is a high-performance, general-purpose I/O interconnect or transfer interface defined for a wide variety of future computing and communication platforms. It enables the connection of non-core components such as graphic cards, memory, etc. to the motherboard. PCIe is governed by the PCI-Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG) and it is available at multiple speeds known as different generations. PCIe Gen1, Gen2, Gen3, Gen4 and Gen5 supports 2.5Gbps, 5Gbps, 8Gbps, 16Gbps and 32Gbps speeds respectively. PCIe supports some advanced features such as Power Management, Quality of Service (QoS), Hot-Plug/hot-swap support, data integrity, and error handling.
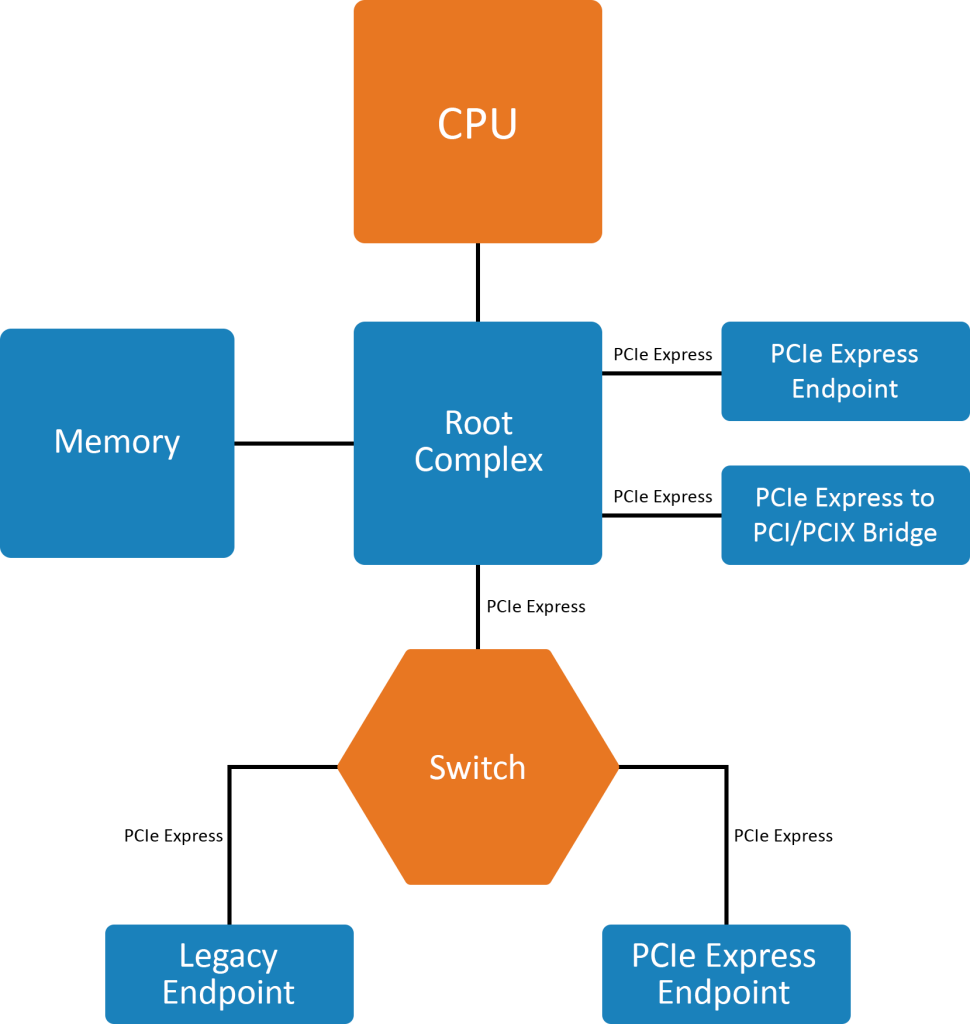
Figure 1- PCIE express example topology
The above figure shows the basic topology of PCIe protocol consisting of a Root Complex (RC), multiple Endpoints (I/O devices), a Switch, and a PCI Express to PCI/PCI-X Bridge. PCIe enables point-to-point connections called links. Each link can support 1 to 32 lanes and each lane consist of 2 pairs of wires, one for transmitting and another for receiving. PCIe implementation can vary depending on the use cases. It can be used to connect ethernet cards, solid-state devices, video cards, and sound cards.
What is NVME?
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVME) is a transfer protocol that works on top of the transfer interfaces such as PCIe. NVMe is governed by the NVM express work group comprising 90 companies. It defines how a host software communicates with the non-volatile memory over a PCIe bus. It is specially designed for accessing high-speed storage media devices which enables the users to leverage the full potential of SSD technology. NVMe can support up to 64k queues and 64k commands per queue whereas traditional HDDs have 1 queue per command.
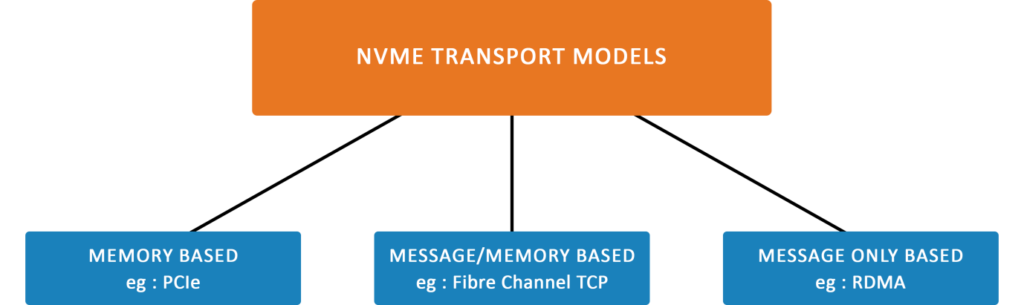
Figure 2-classification of NVME transport model
A host and an NVMe sub-system can communicate through 2 constructs – a memory-based transport model and a message-based transport model. The message-based transport model is again classified as a message-only transport model and a message/memory transport model based on how data is transferred between nodes. In the memory-based transport model, the commands, responses, and data are transferred through explicit memory read and write operations. In the message-only transport model data is transferred using capsules or messages and in the message/memory transport model the command capsules, response capsules, and data are transferred in a combination of messages and explicit read or write operations.
Are NVME and PCIE different?
NVMe is a scalable host controller interface designed to work with PCIe-based solid-state drivers. Each NVMe controller is associated with a PCIe function, and it can support multiple namespaces. Namespace is a quantity of non-volatile memory that may be formatted to a logical block, and they are referenced using a namespace id.
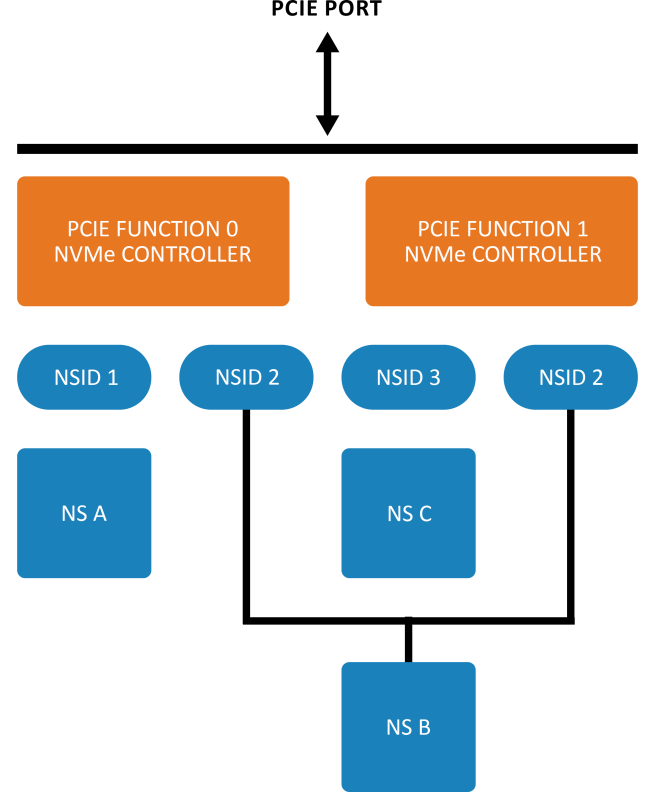
Figure 3 is an example of an NVMe subsystem with 2 controllers, 2 functions, and a single port. PCIe function 0 is associated with one controller and PCIe function 1 is associated with another NMVe controller. Each controller supports a private namespace and a shared namespace. The namespace id can be the same for the shared namespaces. The controllers sharing a namespace can work concurrently and the ordering requirements while issuing the commands to different controllers are handled by the host software or associated application.
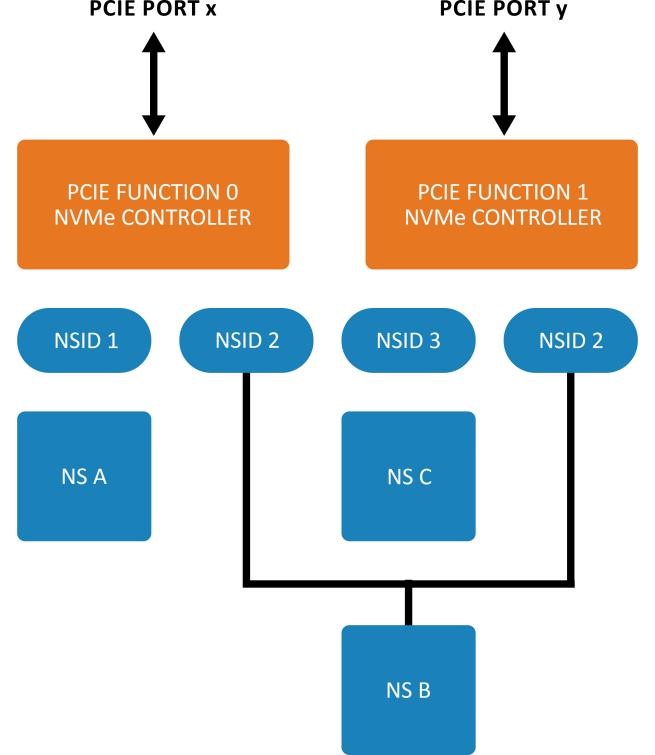
Figure 4 is an example of an NVMe subsystem with 2 controllers,2 functions, and 2 PCIe ports. The main functionality remains the same as in Figure 3 except the subsystem has 2 ports. These 2 PCIE ports can be of the same root complex or different root complex and may be used to implement both multipath I/O and I/O sharing architecture. The ports are completely independent and have their reset and clock. The reset on one controller will not affect the other controller, its shared namespaces, and the operations performed by the other controller in the shared namespace.
So, PCIe and NVMe are not contradictory technologies rather they both work together to utilize the full capabilities of the latest SSDs. The term PCIE SSD implies how the SSD is connected and NVMe is the format and rules on how the data is stored and accessed.
About the Author:
Anjana Menon is a Technical Lead- FPGA Design at Prodigy Technovations. She graduated from Model Engineering College in 2016 with a Bachelor’s Degree in Electronics & Communication Engineering. She has a Master’s Degree in MTech, Microelectronics from Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani.
Prodigy PCIe Protocol Analyzer
Prodigy’s PCIeGen3/4-PA is a PCIe Protocol Analyzer that supports protocol analysis up to PCIe Gen4 speeds. PCIe design and test engineers can easily capture and record traces at 2.5, 5.0, 8 and 16GT/s at a specific event and obtain error reports instantaneously at an affordable price.