UFS is becoming widely used storage device in many different applications smartphone, Tablets, Digital Cameras and Camcorders, Automotive, Augmented Reality and Virtual reality, wearable, augmented devices and hard disk drives. Now it expected to used in laptops in the near future.
UFS stands for Universal Flash Storage. It is type of non-volatile memory which can have a storage capacity of 1TB. This technology is adopted and deployed many leading companies such as Qualcomm, Intel, MediaTek, Kioxia, Samsung, Wester Digital, Micron, Silicon Motion and many more companies. This standard is developed and maintained by JEDEC Solid State technology Association and MIPI alliance . UFS devices are gradually replacing eMMC, SD card and even SSD applications. UFS technology used in many more applications which needs low latency, high speed data transfer and low power consumption. Latest UFS standard is UFS4.0, each lane operates maximum data rate of 23.32Gbps. UFS is based on SCSI architecture and supports SCSI tagged command queuing.
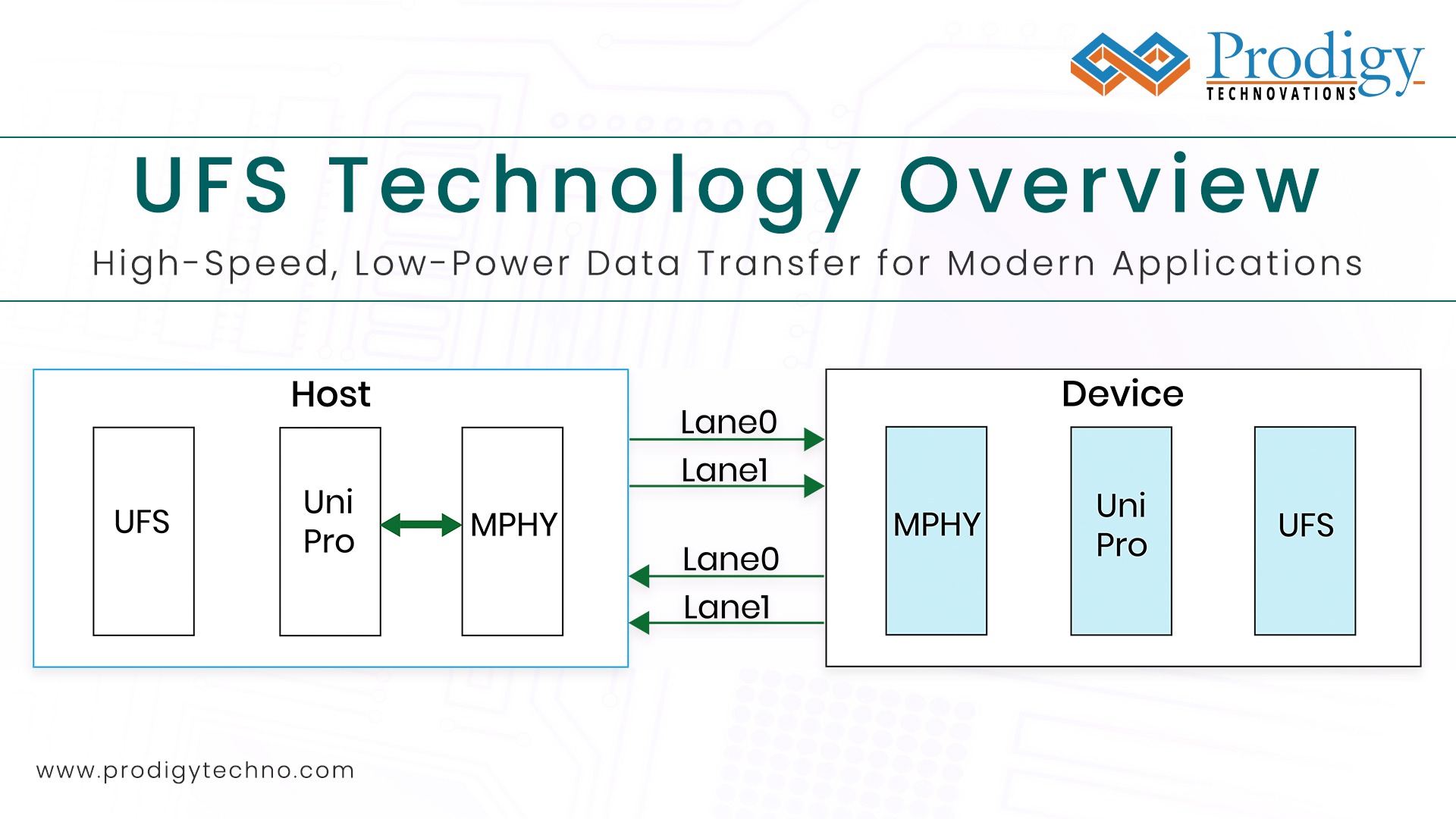
UFS is uses the MPHY for physical layer and UniPro for datalink and transport layer of the protocol. Both MPHY and UniPro Standard is developed and maintained by MIPI Alliance. UFS is available in UFS2.0, UFS2.1, UFS3.0, UFS3.1 and UFS4.0 versions. The main difference between these versions of the UFS standard is data rate and high-performance booster commands.
UFS Protocol is encapsulated in Unipro layer. To understand UFS protocol , we have to know focus on three layers of OSI
- Physical Layer known as MPHY
- Datalink and Transport layer is UniPro
- Application layer is UFS
Host and Device are interfaced using physical layer MPHY. Host manages the read and write operation of UFS device. UFS controller within the manages NAND memory (Flash) with the UFS device.
Data Link layer manages the data transfer between the host and device and vice versa. Dat flow control ensures that data is delivered to the host or device by monitoring the CRC value of the data.
Physical layer manages the encoding of the data, scrambling and packetizing the data received from UniPro layer through the RMMI interface over to host or device using LVDS lines. Advanced power management system in MPHY allows users to program the device to place in hibernate, sleep state, use one or two lane data transmission in different modes.