
eMMC vs UFS
The Differences between eMMC and UFS are:
What is eMMC Protocol?
Embedded multimedia card or eMMC, is a NAND flash memory for mobile applications and a memory solution for consumer electronics such as tablets, smartphones, GPS systems, eReaders, and other mobile computing devices.
What is UFS Protocol?
Universal Flash memory or UFS is the next generation of Flash memory. UFS is providing flash memory with high data transfer speed, high reliability, and low power consumption. The UFS standard is managed and developed by the JEDEC. UFS 4.0, the most advanced JEDEC standard, offers sequential read-write speeds to support live streaming and augmented reality applications in mobile devices. UFS will be the next-generation flash memory standard for automotive applications as well.
What is the difference between eMMC and UFS ( eMMC vs UFS )?
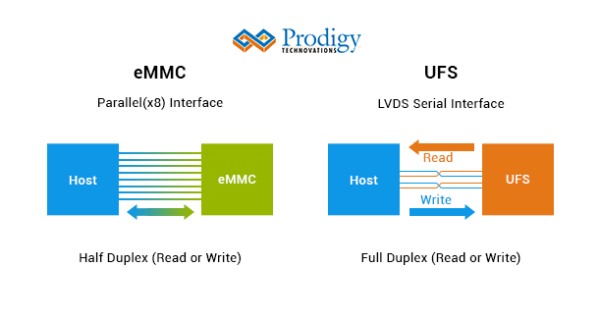
- UFS has Low voltage differential Signalling (LVDS) signaling interface.
- UFS has a command Queue (CQ) to sort out commands to be carried out and allow multiple commands to be carried out.
- eMMC is half-duplex hence either read or write into the memory is possible.
- UFS is a full-duplex interface and allows simultaneous read and write.
- eMMC is slower than UFS.
- UFS supports advanced features like Deep Sleep, write booster, and throttling notifications to the host.
Advantage eMMC
-
Cost: eMMC continues to be cheaper and most widely used in smartphones and most consumer devices as storage devices.
Advantage UFS :
- Speed: UFS 4.0 can support bandwidth up to 4800 MB/s
What is the Protocol Analyzers to Debug eMMC Protocol and UFS Protocol?
Prodigy offers a protocol analyzer to capture and monitor eMMC and UFS packets. Prodigy’s eMMC protocol analyzer and UFS 4.0 protocol analyzer has the advanced capability not only to trigger but long allow very long captures which is very useful for the embedded design engineer during the debug. UFS4.0 protocol analyzer comes with advanced series of probes to capture high-speed signals.




