Understanding Clock Stretching in I²C Communication and How PGY-I2C-EX-PD Simplifies Debugging
Efficient communication between devices is crucial in modern embedded systems, especially when using protocols like I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit). One of the key mechanisms that ensures smooth data transfer between fast masters and slower slaves is clock stretching. This blog explores the importance of clock stretching, the challenges engineers face, and how the PGY-I2C-EX-PD tool provides effective solutions.
What is Clock Stretching and Why Is It Important?
In I²C communication, the master device generates a clock signal to synchronize data exchange with slave devices. However, some slave devices may require additional time to process data or respond to commands. Clock stretching allows these slower slaves to hold the clock line low temporarily, pausing communication until they are ready. This mechanism prevents errors such as missed data or corrupted transmissions.
Without clock stretching, mismatches in timing could lead to unreliable operation of sensors, memory devices, or other peripherals. Understanding and debugging clock stretching events is critical for ensuring error-free communication in complex systems.
Challenges Engineers Face with Clock Stretching
Data Corruption: If the master sends or requests data before the slave is ready, it can result in incorrect or lost data.
Missed Responses: Slaves that fail to acknowledge (ACK) within the expected timeframe may cause the master to assume communication failure.
Timing Mismatches: Certain devices need extra processing time that may not align with the master’s clock speed.
Hard-to-Debug Errors: Random failures caused by timing mismatches can be difficult to trace without proper tools.
These challenges highlight the need for tools that provide flexibility in testing and debugging I²C setups.
How PGY-I2C-EX-PD Solves Clock Stretching Issues
The PGY-I2C-EX-PD tool is designed specifically to address these challenges, offering engineers a comprehensive solution for analyzing and optimizing I²C communication. Here are its key features:
Flexible Clock Stretch Timing:
Engineers can define custom durations for clock stretching during ACK/NACK and data phases, allowing slaves sufficient time for processing.
This flexibility helps validate the performance of both master and slave devices under varied conditions.
Waveform & Protocol Decoding:
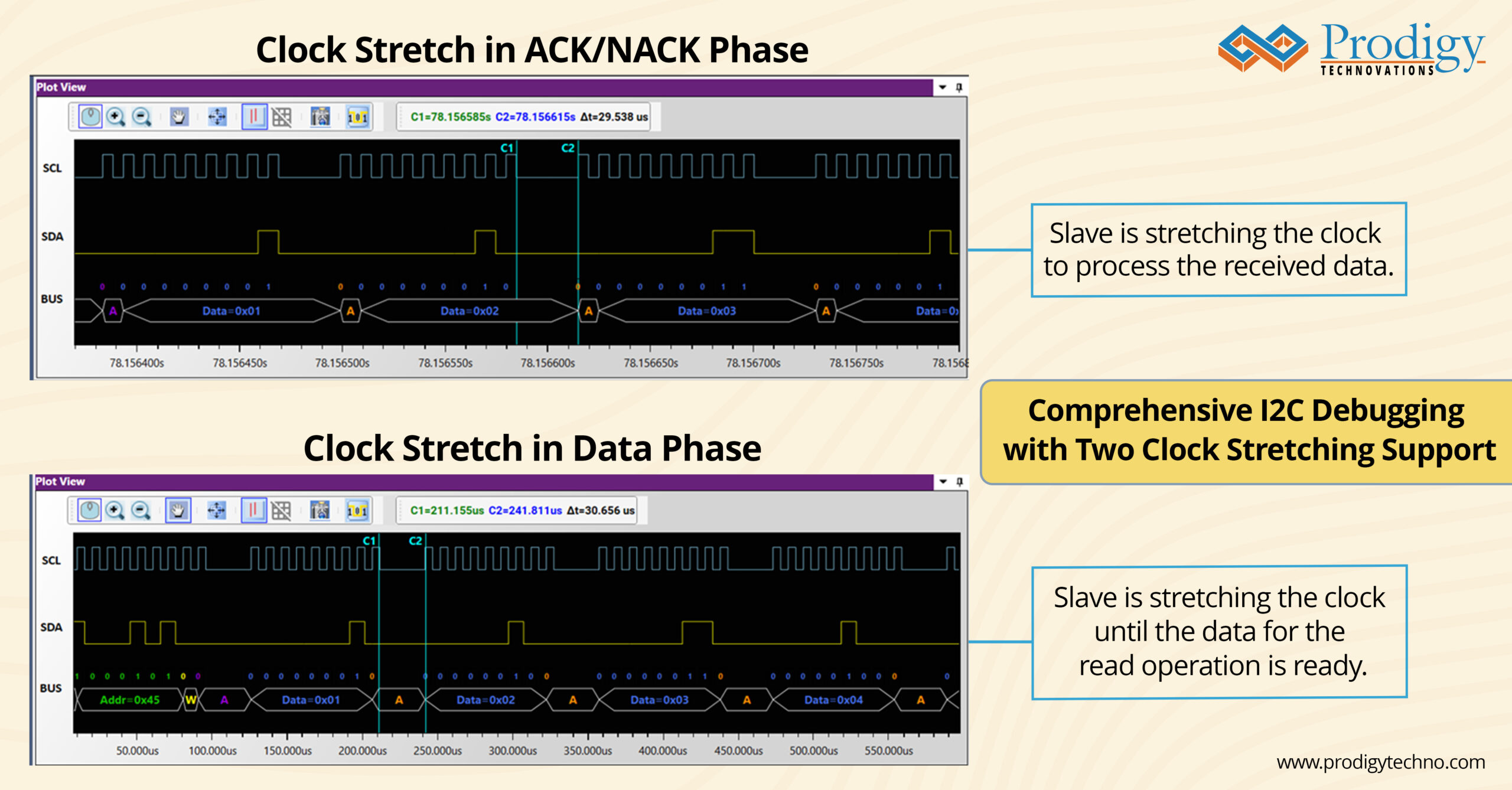
The tool provides clear visual representations of clock stretching events during data transfer phases. These visualizations make it easier to identify where timing mismatches occur.
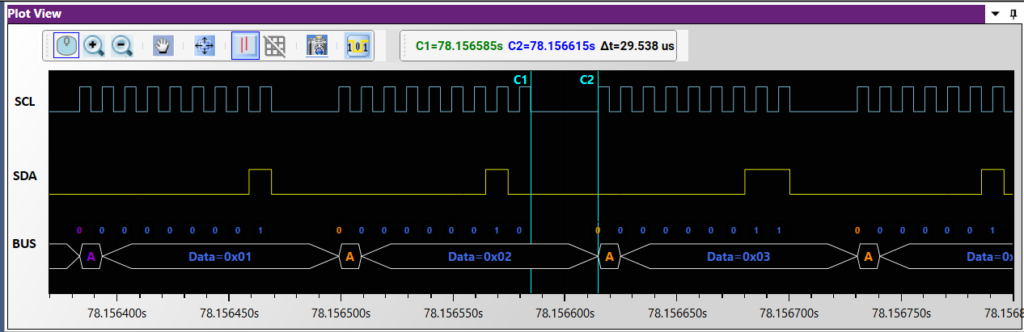
(i) Slave is stretching the clock to process the received data.
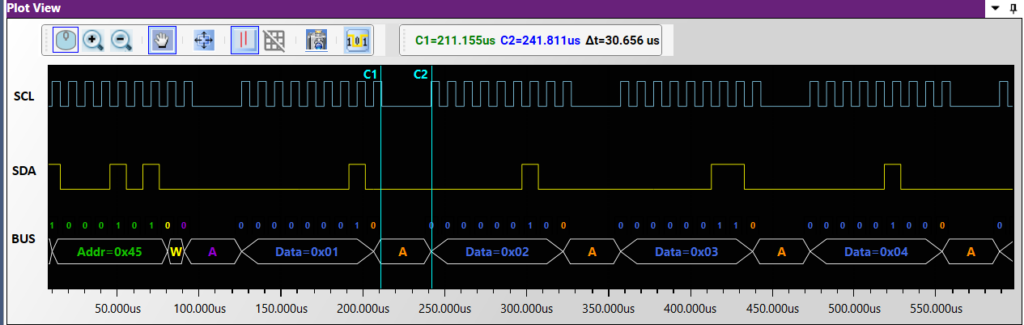
(ii) Slave is streatching the clock until the read operation’s data is ready.
Accurate Timing Measurements:
PGY-I2C-EX-PD measures how long a slave holds the clock line low, enabling precise analysis of timing issues.
By leveraging these capabilities, engineers can ensure seamless communication between fast masters and slow slaves while minimizing errors.
Conclusion
Clock stretching is an essential feature of I²C communication that ensures reliable operation across devices with varying processing speeds. However, debugging clock stretching events can be challenging without the right tools. The PGY-I2C-EX-PD simplifies this process by offering flexible timing configurations, waveform decoding, and accurate measurements.
With PGY-I2C-EX-PD, engineers can confidently analyze, debug, and optimize their systems for smooth data flow making it an indispensable tool for modern embedded system development.



