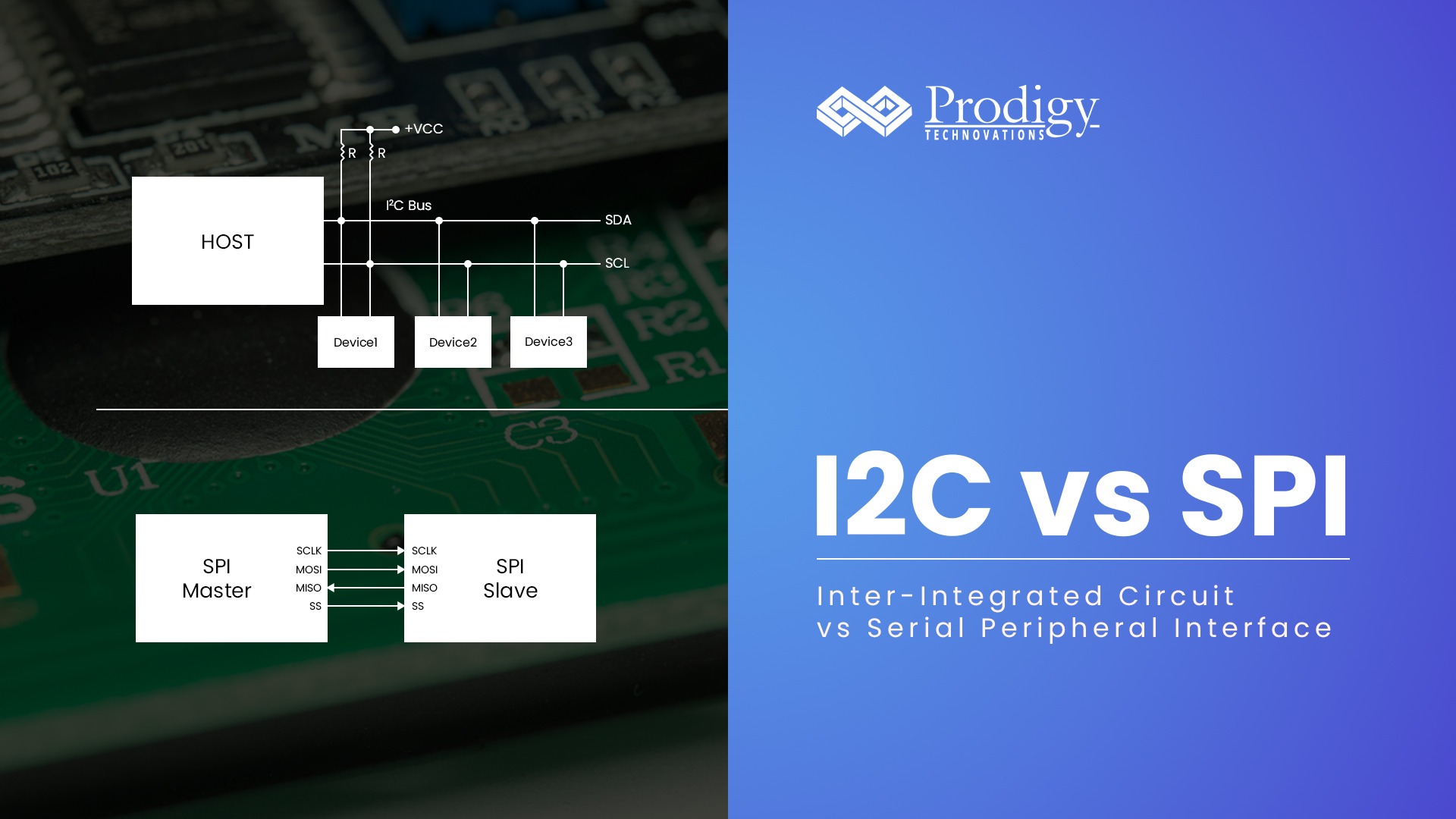
I2C vs SPI Difference Between I2C vs SPI What is I2C Protocol? I2C stands for Inter-Integrated Circuit. I2C is a simple two-wire serial protocol used to communicate between two...
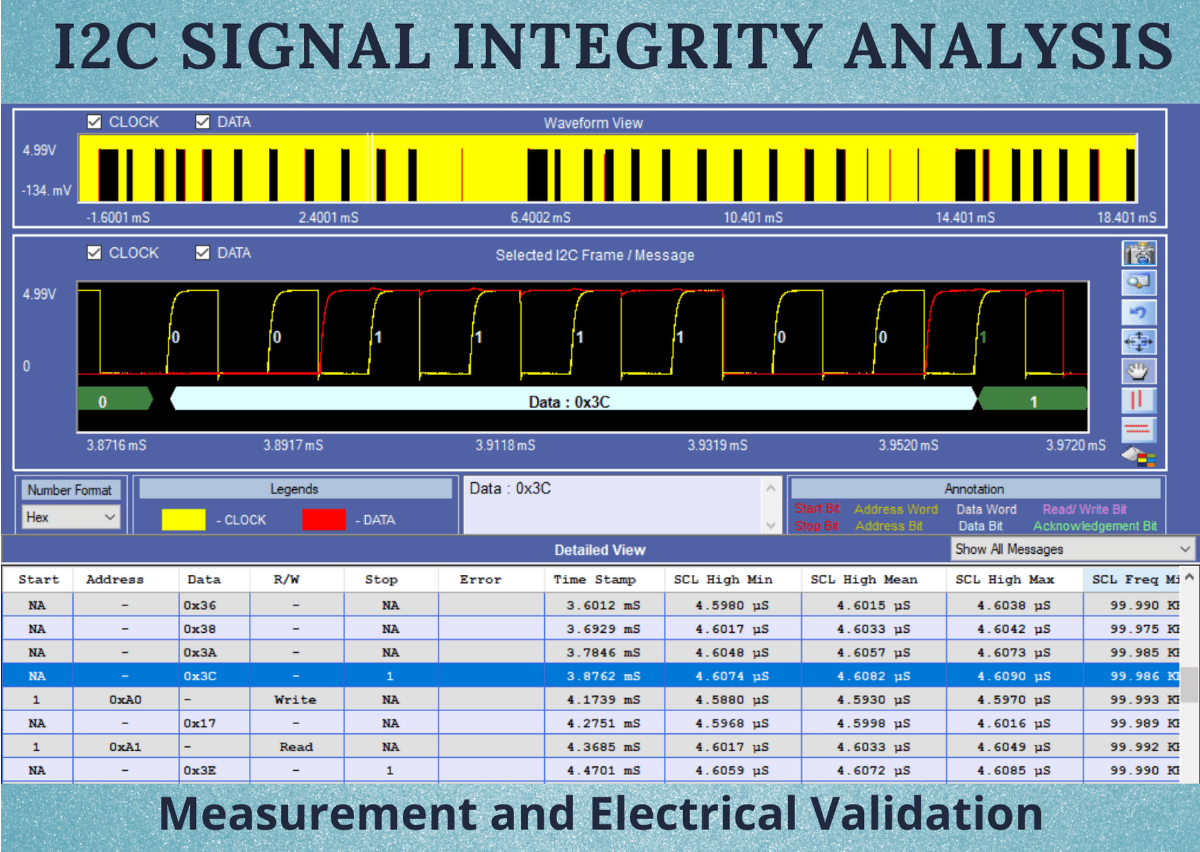
I2C Signal Integrity: Measurement and Electrical Validation Overview of I2C Bus: The I2C’s physical two-wire interface consists of a bi-directional serial clock (SCL) and data (SDA) lines. Each device...
I2C Bus Introduction to I2C Bus: I2C stands for Inter-Integrated Circuit. Philips Semiconductors developed I2C in the early 1980s as a low-cost solution for connecting lower-speed peripheral ICs to...
I2S Protocol I2S Protocol Introduction Today’s digital systems – from the Digital TV in the living room, Alexa, and google home for playing music and switching from text-based search...
I2C vs I2S Difference between I2C vs I2S What is I2C Protocol? I2C stands for Inter IC communication. I2C is a simple two-wire protocol used to comminute between two...
eMMC vs UFS The Differences between eMMC and UFS are: What is eMMC Protocol? Embedded multimedia card or eMMC, is a NAND flash memory for mobile applications and a...
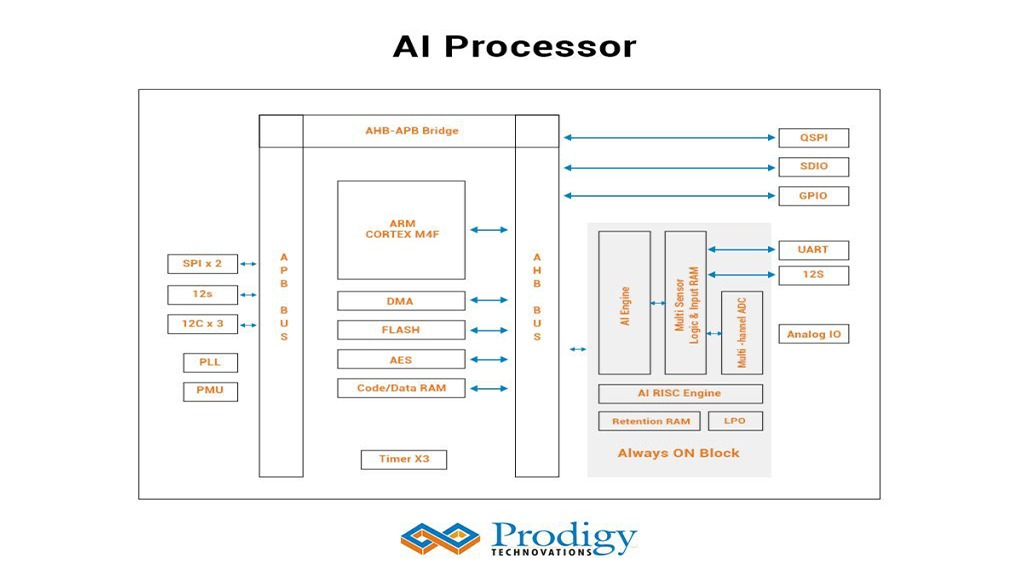
How did the AI Edge voice chip Company accelerate the Post Silicon bring up? INTRODUCTION A startup was working on AI Edge-based voice processor chip. The voice-based AI chip...
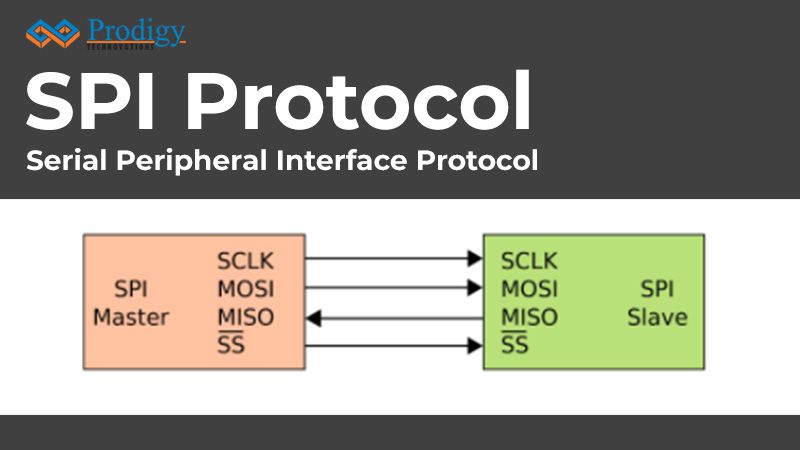
SPI PROTOCOL SPI Protocol: Introduction SPI stands for Serial Peripheral Interface and it is a synchronous serial communication interface used for short-distance communication. SPI interface was developed by Motorola...
HDMI Protocol Introduction HDMI is a digital replacement for existing analog video standards. It is termed as the catalyst for the DTV revolution. The DTV revolution is driving the...
UART PROTOCOL UART Protocol: INTRODUCTION UART stands for Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter. A UART’s main purpose is to transmit and receive serial data. UART was developed by Gordon Bell...