eSPI Protocol eSPI Protocol INTRODUCTION eSPI stands for the enhanced serial peripheral interface. It was developed by Intel. eSPI is an all-in-one bus that was designed to replace the...
What is a Protocol Analyzer? A Protocol Analyzer is a measurement tool or device used to capture and monitor data over a communication channel. It captures the data on...
PCI Express (PCIe or PCI-e) Introduction to PCIe Express: This blog describes the fundamentals of the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCI Express) protocol. In personal computers, peripheral devices connect...
UFS Protocol Introduction: UFS stands for Universal Flash Storage. UFS is an advanced, high speed, low power, high-performance non-volatile interface designed for mobile systems such as smartphones and tablets...
MDIO (Management Data Input/Output) Introduction to MDIO: Management Data Input/Output (MDIO), or Media Independent Interface Management (MIIM) is a serial bus protocol defined for the IEEE 802.3 standard Ethernet...
DDR5 I3C What is the role of the I3C Protocol in DDR5? DDR5 has significant improvement over DDR4. DDR5 offers higher bandwidth with a data rate of up to...
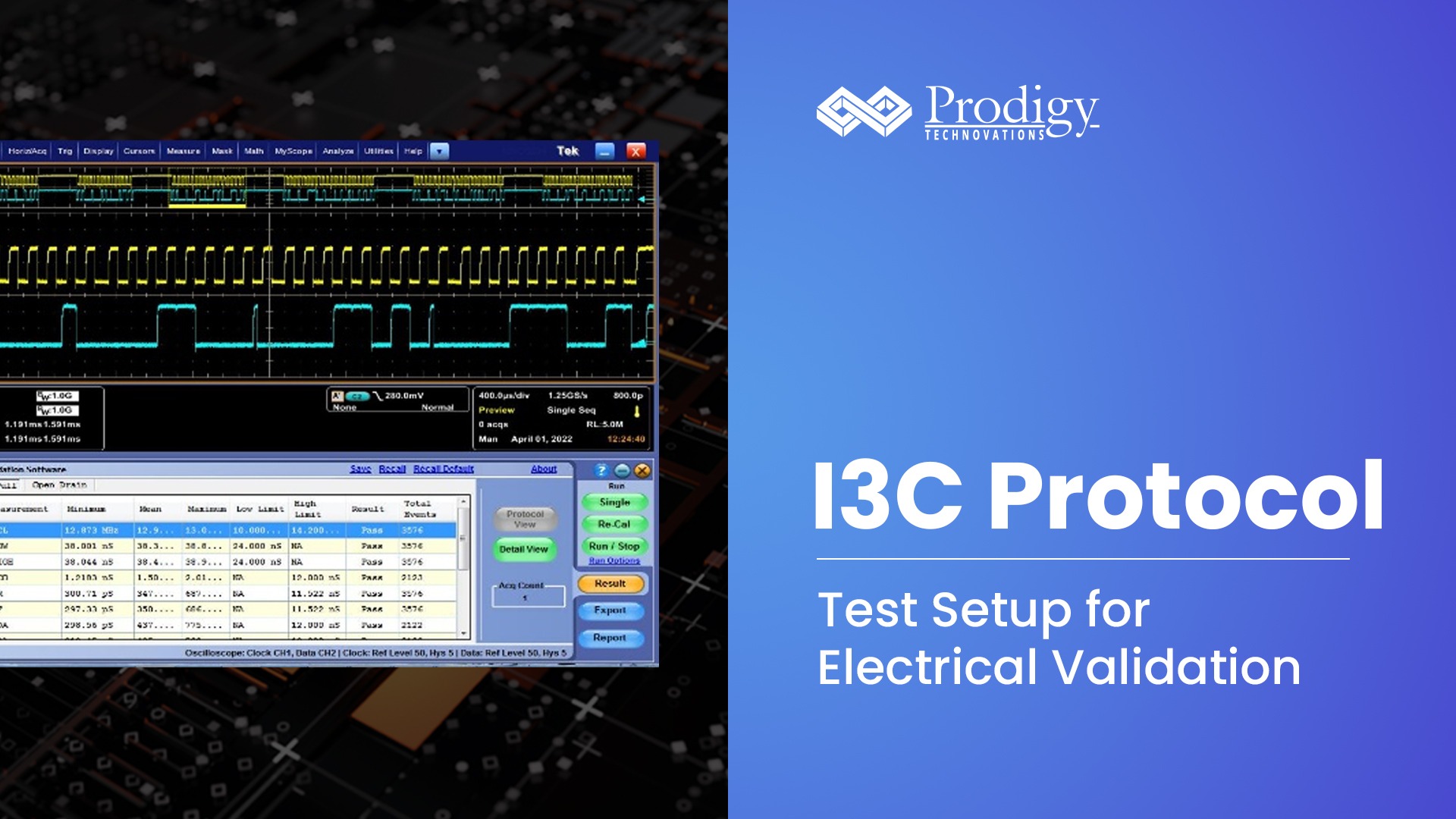
I3C Protocol: Test Setup for Electrical Validation I3C devices are going through mass adoption at the moment. One challenge however remains for I3C devices is interoperability. The I3C devices...
The CHIPS Act of 2022 – Shaping the New Semiconductor Market. On July 28, 2022, congress passed the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 to strengthen the domestic manufacturing...
I2C Clock Stretching Introduction: I2C Protocol I2C Protocol stands for Inter Integrated-Circuit. I2C is a simple two-wire design, half-duplex serial communication protocol, and the data is transmitted bit by...
SMBus Protocol SMBus Protocol Introduction: The System Management Bus (SMBus) is a two-wire interface through which various system component chips and devices can communicate with each other and with...