Embedded Debug Time Challenge Introduction Embedded development has many activities like board bring-up, device driver development, RTOS or kernel bring up and finally giving the board to the application...
HOW TO SELECT THE RIGHT PROBES FOR DEBUGGING? Debugging design in embedded systems is quite complex and Logic analyzers play a very important role to expedite the debugging and...
eMMC Protocol An eMMC Protocol (embedded Multi-Media Controller Protocol) Flash device is a non-volatile, rewritable mass storage device. Both flash memory and controller are included in a single integrated...
TRIGGERING FUNDAMENTALS – LOGIC ANALYZER TRIGGERS WHAT IS TRIGGERING? The triggering feature allows engineers to capture a particular event of interest or data. Logic analyzers can be triggered on...
SDIO Protocol: SDIO Protocol is a widely used Bus for the interfacing modem (device) to the application processor (Host). SDIO Protocol is used for Data exchange between host and...
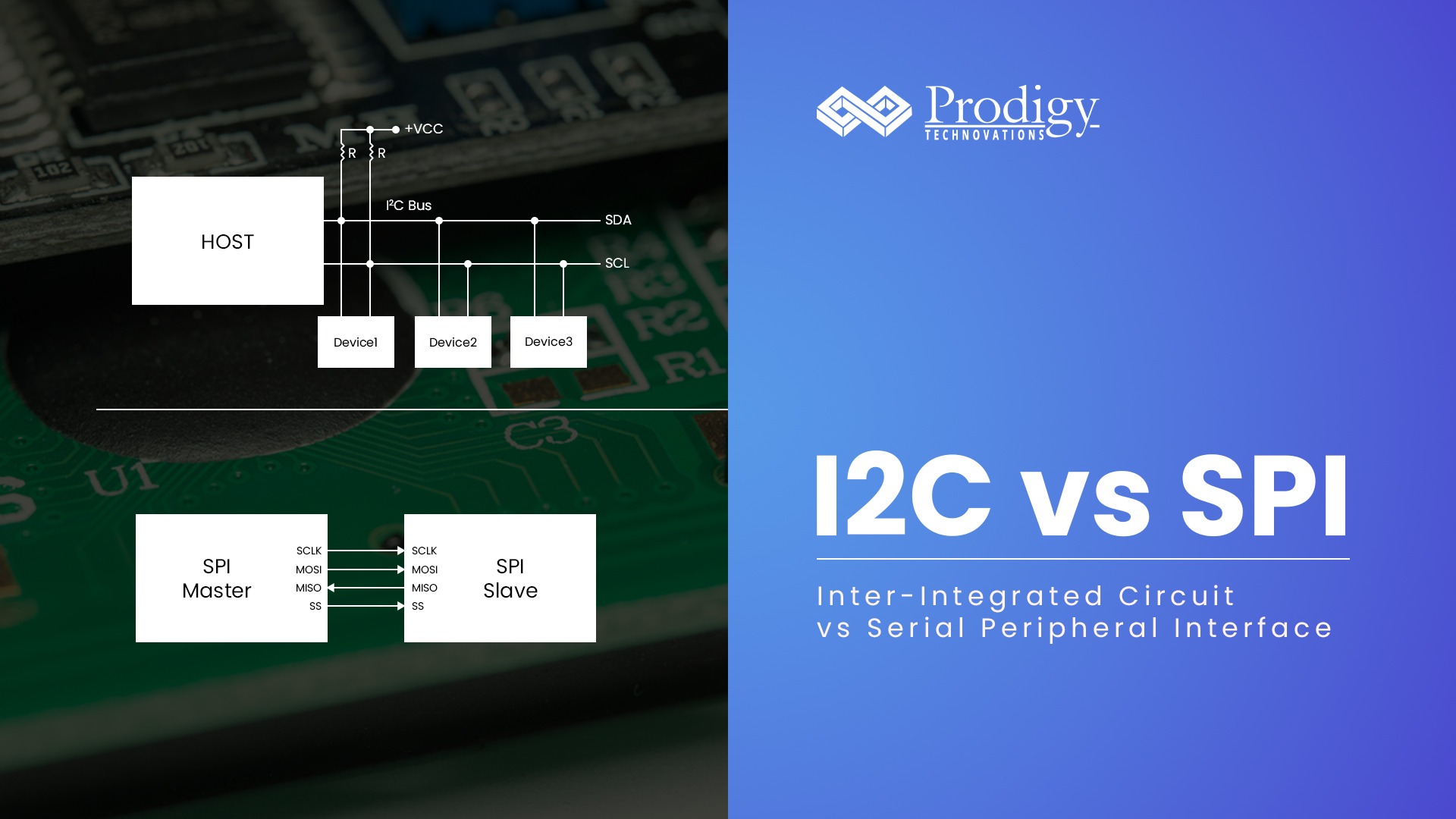
I2C vs SPI Difference Between I2C vs SPI What is I2C Protocol? I2C stands for Inter-Integrated Circuit. I2C is a simple two-wire serial protocol used to communicate between two...
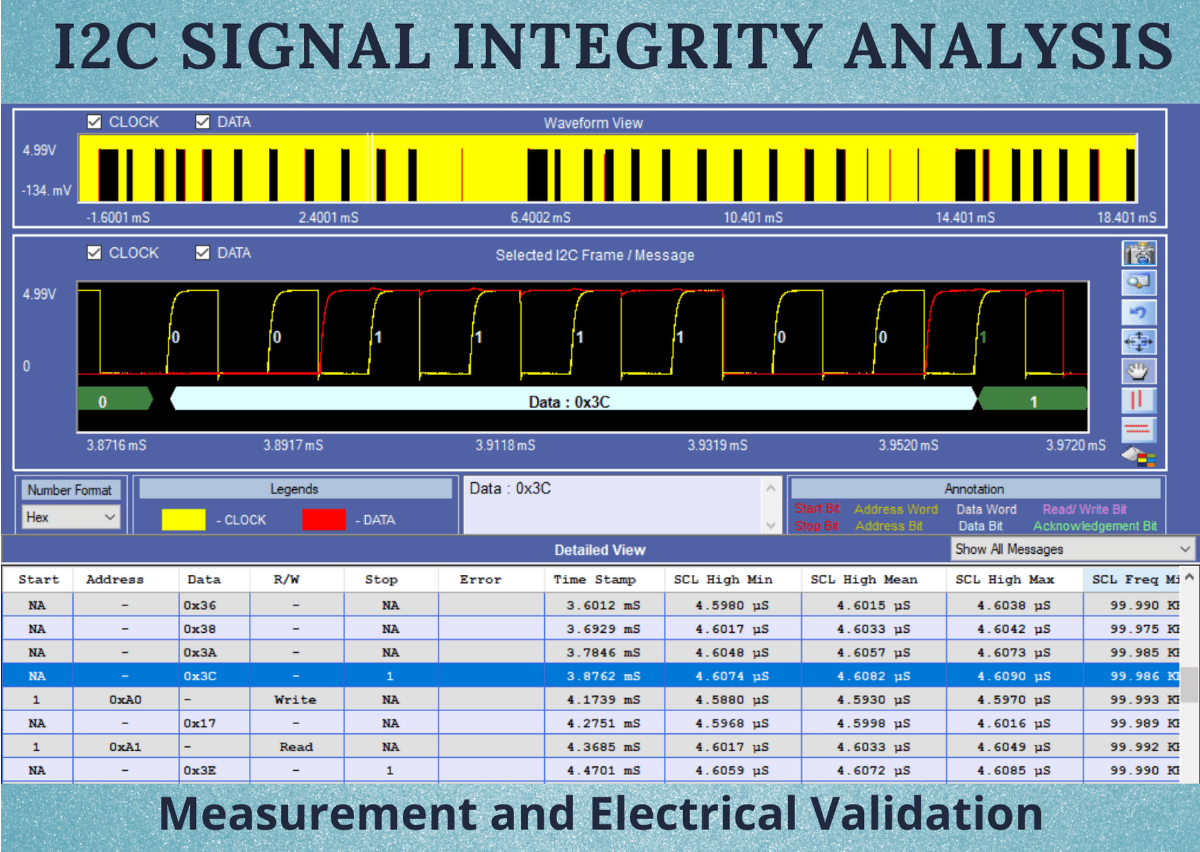
I2C Signal Integrity: Measurement and Electrical Validation Overview of I2C Bus: The I2C’s physical two-wire interface consists of a bi-directional serial clock (SCL) and data (SDA) lines. Each device...
I2C Bus Introduction to I2C Bus: I2C stands for Inter-Integrated Circuit. Philips Semiconductors developed I2C in the early 1980s as a low-cost solution for connecting lower-speed peripheral ICs to...
I2S Protocol I2S Protocol Introduction Today’s digital systems – from the Digital TV in the living room, Alexa, and google home for playing music and switching from text-based search...
I2C vs I2S Difference between I2C vs I2S What is I2C Protocol? I2C stands for Inter IC communication. I2C is a simple two-wire protocol used to comminute between two...